What Is the Function of Macromolecule Subunit Below
Another question on Biology. Humans and other organisms are able to consume these macromolecules within the foods we eat every day as well as manufacture some of.

Bio Eoc Review Ms Idris Ppt Download
Each of these four has their own unique chemical structure and their own specific function within living organisms.
. Composes the majority of the cell membrane. Each macromolecule type has its own structure and function. What is the function or macromolecule subunit below.
Environmental factors can determine if a genetic trait becomes a health issue. The macromolecule shown in the image represents nucleotide as it consist of one phosphate one pentose sugar and one nitrogenous Base. Proteins are made of monomers called _____ answer choices.
Provide structural supporttransport enzymes movement defense. Proteins lipids carbohydrates and nucleic acids. The monomer units of macromolecules are polar in nature with their heads and tails with different physical and chemical properties.
Sets found in the same folder. Macromolecular structure determines function and regulation. Properties structure and function of biological macromolecules.
You will recall that molecules are a collection of atoms connected by covalent bonds. What is the function of the macromolecule subunit below. There are four basic kinds of biological macromolecules.
Stores genetic information D. The enzymes will require less energy to function than at 70 group H carboxyl group General structure of an ex -amino acid. There are 4 major biological macromolecules.
What is the function of the macromolecule subunit below. Protein functions include structural support storage transport cellular signaling movement and defense against foreign substances. Adenosine guanine cytosine uracil and thymine.
They may serve in transport storage or membranes. Composes the majority of the cell membrane. Macromolecules are also termed as polymers.
What is the function of the macromolecule subunit below. Any reaction catalyzed by and enzyme or any catalyst is energetically. They consist of nucleotide polymers.
They are necessary for energy storage. DNA contains the genetic components and instructions in a cell while RNA is used by the cell to make proteins. While there is no standard definition of how large a molecule must be to earn the macro prefix they generally have at a minimum thousands of atoms.
Stores genetic information. Students should be able to explain and apply core concepts of macromolecular structure and function including the nature of biological macromolecules their interaction with water the relationship between structure and function and frequently encountered mechanisms for regulating their function. The activation energy is the amount of energy you need to add to the substrates or reagents in order to react and form a product.
Most important protein enzymes function as catalysts in cells regulating metabolism by selectively accelerating. Carbohydrates are also called saccharides and their monomers are. Stores genetic information D.
Many macromolecules are polymers of smaller molecules called monomers. A macromolecule is a very large molecule usually consisting of repeated subunits called monomers which cannot be reduced to simpler constituents without sacrificing the building block element. What is the function of macromolecule subunit below.
The nucleotides are found in Nucleic acids DNA and RNA that functions to store genetic information and transfer it to next generation. Their primary function is as a source of energy. A biological macromolecule DNA or RNA composed of the elements C H N O and P that carries genetic information.
Building blocks of protein. Environmental factors determine all genetic traits. Dehydration synthesis or a condensation reaction.
They are found in all living things on Earth. Stores genetic information. Cells readily convert carbohydrates to usable energy.
What is the function of macromolecule subunit below. Which of the following macromolecules contains these monomers. The above structure is that of a nucleotide phosphate nitrogenous base sugar which corresponds to the building block of nucleic acids namely DNA.
The most common macromolecules in biochemistry are biopolymers and large non-polymeric molecules such as. Nucleic acids are DNA and RNA. Dehydration synthesis or a condensation reaction.
Composes the majority of the cell membrane. Proteins may be structural regulatory contractile or protective. How do environmental factors influence genetic traits.
Composes the majority of the cell membrane. Insulator and stores fat and energy. Composes the majority of the cell membrane.
Or they may be toxins or enzymes. The diagram below shows a monomer of a macromolecule. A macromolecule is a very large molecule important to biophysical processes such as a protein or nucleic acid.
Macromolecules are so huge that these are made up of more than 10000 or more atoms. Carbohydrates lipids proteins and nucleic acids. Biology is brought to you with support from the Amgen Foundation.
Store energy provide fuel and build structure in body main source of energy structure of plant cell wall. Composes the majority of the cell membrane. These polymers are composed of different monomers and serve different functions.
Proteins are one of the most abundant organic molecules in living systems and have the most diverse range of functions of all macromolecules. Organic molecules made of carbon hydrogen and oxygen and store food energy until needed fats nucleic acid. They are formed by the polymerisation of molecules such as carbon hydrogen and oxygen.
What is the function of macromolecule subunit below. They are composed of thousands of covalently bonded atoms. Molecules composed of sugar monomers.
Stores and transfers info. That is they lower the activation energy of a given reaction so it can occur.

What Is The Function Of The Macromolecule Subunit Below Brainly Com
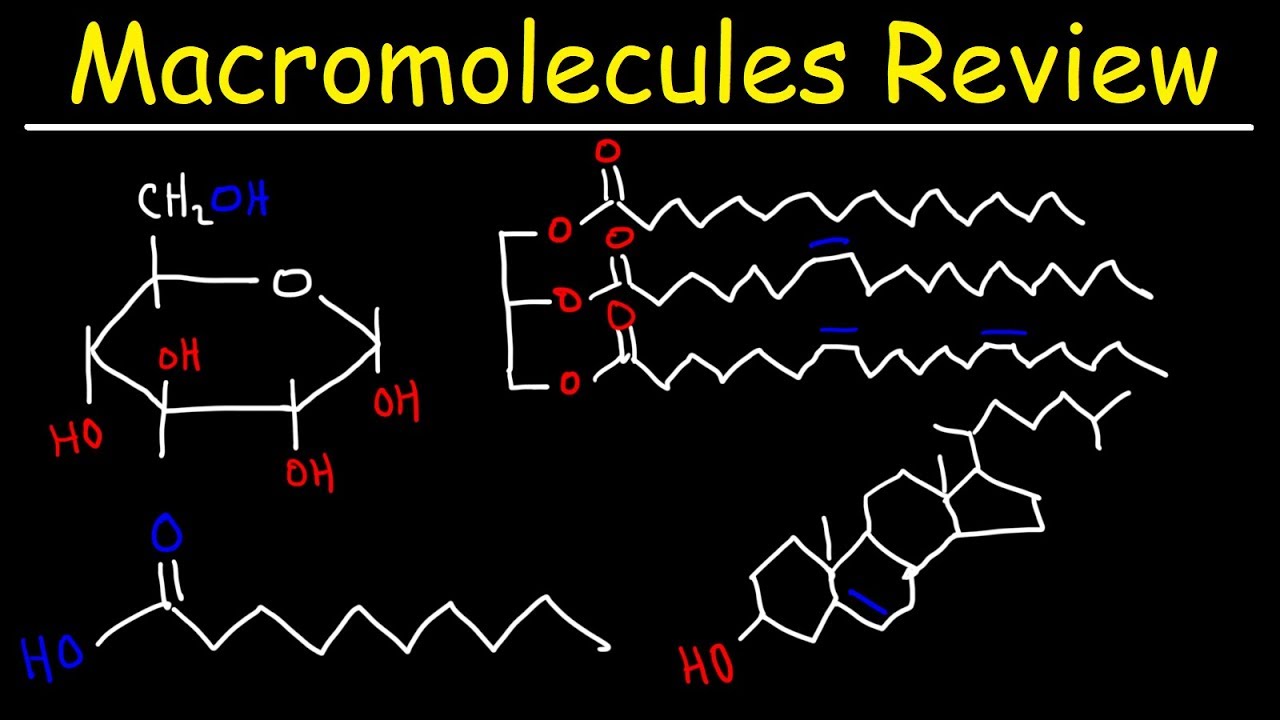
What Is The Function Of The Macromolecule Subunit Below Lisbdnet Com
Comments
Post a Comment